Services
 Polysomnogram - Sleep Study
Polysomnogram - Sleep Study
What to Expect:
POLYSOMNOGRAM (PSG): This is the most common test. During the PSG, there is continuous monitoring of brain activity, breathing and of leg movements during sleep. This test allows the sleep specialist to diagnose the more common problems of sleep such as sleep apnea and periodic leg movements.

CPAP TITRATION ANALYSIS: If there is evidence for sleep apnea, you will be called back for continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) titration. This involves placing a mask over the nose and blowing in air at pressure to help prevent snoring and apnea. The pressure is gradually titrated upwards to find the right settings.
MSLT: The Multiple Sleep Latency Test (MSLT) is carried out during the daytime and assesses the rapidity with which an individual falls asleep. This test is useful when studying the reasons for daytime sleepiness.
MWT: Maintenance of Wakefulness Test (MWT) helps to determine how well an individual can resist falling asleep.
For more information visit:
www.aasmnet.org
How to Prepare for Sleep Study:
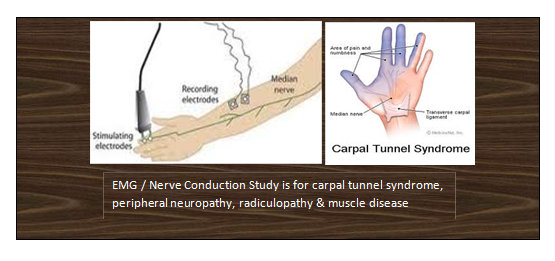
Electromyography/Nerve Conduction Study EMG/NCS
What to Expect:

EMG/NCS is a test used to investigate symptoms such as numbness, tingling, weakness and back/neck/limb pains. The test measures the electrical activity in muscles and nerves, and helps determine if there is damage to these structures. EMG/NCS is usually done if there is a suspicion of carpal tunnel syndrome, a pinched nerve in the neck or back, nerve damage in the feet as in neuropathy, or for muscle damage as in myopathy.
For additional information visit:
http://www.aanem.org/Education/Patient-Resources/Learn-About-an-EMG.aspx
How to prepare for EMG/NCS
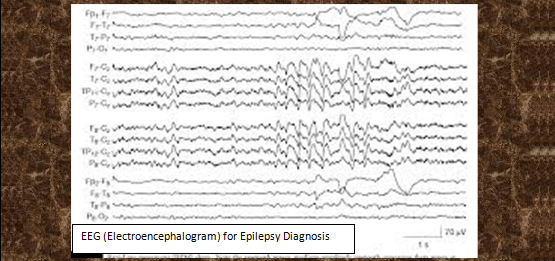
Electroencephalogram
What to Expect:
EEG is used to investigate for abnormal electrical signals arising from the brain. The test is oftentimes needed to evaluate symptoms such as fainting or black out spells, seizures and epilepsy.
For more information visit:
www.epilepsyfoundation.org/index.cfm
How to Prepare for Routine or Sleep Deprived EEG
How to Prepare for Ambulatory EEG
 Polysomnogram - Sleep Study
What to Expect:
POLYSOMNOGRAM (PSG): This is the most common test. During the PSG, there is continuous monitoring of brain activity, breathing and of leg movements during sleep. This test allows the sleep specialist to diagnose the more common problems of sleep such as sleep apnea and periodic leg movements.
Polysomnogram - Sleep Study
What to Expect:
POLYSOMNOGRAM (PSG): This is the most common test. During the PSG, there is continuous monitoring of brain activity, breathing and of leg movements during sleep. This test allows the sleep specialist to diagnose the more common problems of sleep such as sleep apnea and periodic leg movements.
 CPAP TITRATION ANALYSIS: If there is evidence for sleep apnea, you will be called back for continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) titration. This involves placing a mask over the nose and blowing in air at pressure to help prevent snoring and apnea. The pressure is gradually titrated upwards to find the right settings.
MSLT: The Multiple Sleep Latency Test (MSLT) is carried out during the daytime and assesses the rapidity with which an individual falls asleep. This test is useful when studying the reasons for daytime sleepiness.
MWT: Maintenance of Wakefulness Test (MWT) helps to determine how well an individual can resist falling asleep.
For more information visit:
www.aasmnet.org
How to Prepare for Sleep Study:
Electromyography/Nerve Conduction Study EMG/NCS
What to Expect:
CPAP TITRATION ANALYSIS: If there is evidence for sleep apnea, you will be called back for continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) titration. This involves placing a mask over the nose and blowing in air at pressure to help prevent snoring and apnea. The pressure is gradually titrated upwards to find the right settings.
MSLT: The Multiple Sleep Latency Test (MSLT) is carried out during the daytime and assesses the rapidity with which an individual falls asleep. This test is useful when studying the reasons for daytime sleepiness.
MWT: Maintenance of Wakefulness Test (MWT) helps to determine how well an individual can resist falling asleep.
For more information visit:
www.aasmnet.org
How to Prepare for Sleep Study:
Electromyography/Nerve Conduction Study EMG/NCS
What to Expect:
 EMG/NCS is a test used to investigate symptoms such as numbness, tingling, weakness and back/neck/limb pains. The test measures the electrical activity in muscles and nerves, and helps determine if there is damage to these structures. EMG/NCS is usually done if there is a suspicion of carpal tunnel syndrome, a pinched nerve in the neck or back, nerve damage in the feet as in neuropathy, or for muscle damage as in myopathy.
For additional information visit:
http://www.aanem.org/Education/Patient-Resources/Learn-About-an-EMG.aspx
How to prepare for EMG/NCS
Electroencephalogram
What to Expect:
EEG is used to investigate for abnormal electrical signals arising from the brain. The test is oftentimes needed to evaluate symptoms such as fainting or black out spells, seizures and epilepsy.
For more information visit:
www.epilepsyfoundation.org/index.cfm
How to Prepare for Routine or Sleep Deprived EEG
How to Prepare for Ambulatory EEG
EMG/NCS is a test used to investigate symptoms such as numbness, tingling, weakness and back/neck/limb pains. The test measures the electrical activity in muscles and nerves, and helps determine if there is damage to these structures. EMG/NCS is usually done if there is a suspicion of carpal tunnel syndrome, a pinched nerve in the neck or back, nerve damage in the feet as in neuropathy, or for muscle damage as in myopathy.
For additional information visit:
http://www.aanem.org/Education/Patient-Resources/Learn-About-an-EMG.aspx
How to prepare for EMG/NCS
Electroencephalogram
What to Expect:
EEG is used to investigate for abnormal electrical signals arising from the brain. The test is oftentimes needed to evaluate symptoms such as fainting or black out spells, seizures and epilepsy.
For more information visit:
www.epilepsyfoundation.org/index.cfm
How to Prepare for Routine or Sleep Deprived EEG
How to Prepare for Ambulatory EEG